What Do Eggs Do In Your Body?
Advertisement
Eggs are one of the most nutritionally dense foods you can eat. Low in calories, high in protein and packed with essential vitamins, minerals and trace elements, eggs make an incredibly nutritious breakfast!
Although eggs once had a bad reputation due to their dietary cholesterol content, recent research has shown that they do not increase the risk of heart disease or stroke.
Proteins
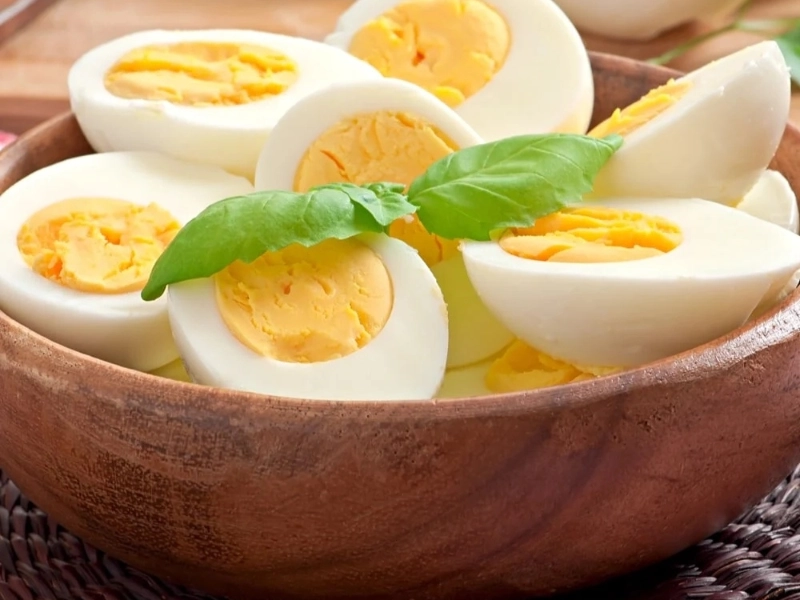

Protein is an essential nutrient that your body needs to build and maintain healthy tissues. It not only keeps your muscles strong and fit but also improves the immunity of those around you. Protein plays a significant role in keeping our systems running efficiently.
Eggs are an excellent source of protein, with just one large egg providing 6-7 grams. The yolk provides 17% and the white (albumin) provides 11%.
Another advantage of protein is its ability to stimulate muscle protein synthesis. Studies have shown that eating eggs as part of a whey protein diet provides greater anabolic stimulation than consuming soy or wheat alone.
Eggs are an excellent source of choline, an essential nutrient that supports brain health and reduces the risk of neurological disorders. Additionally, eggs contain high amounts of phospholipids that help reduce inflammation.
Vitamins
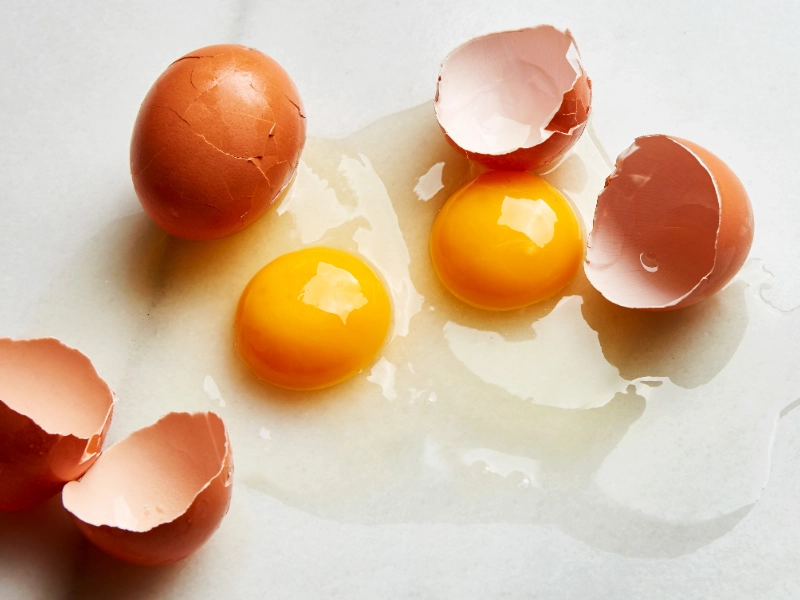

Vitamins are essential for the body, from repairing cellular damage to converting food into energy and keeping bones strong. In addition, vitamins help prevent diseases and improve well-being.
Eggs are an excellent source of many essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin A, B2 (riboflavin), B12, vitamin D, and selenium. Additionally, they contain small amounts of omega-3 fatty acids that promote brain function and eye health.
Some eggs are fortified with niacin and folic acid to meet the dietary needs of pregnant women. In addition, they provide a large amount of choline that helps in fetal brain cell development and prevents birth defects in babies.
Eggs provide a variety of minerals and trace elements, such as zinc, iron, phosphorus, selenium, iodine, copper, magnesium. They also supply lutein and zeaxanthin - two carotenoids especially beneficial for your eyes - which together can protect against cataracts and age-related macular degeneration while improving vision and eye health.
Minerals

Minerals are necessary elements that your body uses for many functions. These include maintaining bones, muscles, teeth; produce hormones; as well as controlling brain cardiac activity.
Minerals can be found in a variety of foods. They are divided into two categories depending on the amount your body requires: macrominerals and trace elements.
Macrominerals are the largest and most significant minerals. These include calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium chloride and phosphorus.
Trace elements refer to smaller elements, such as iron, copper, selenium, zinc, chromium, cobalt fluorine.
To ensure you get all the minerals you need, aim for a balanced diet that includes plenty of dark leafy vegetables, lean meat, fish, poultry as well as whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds and dairy products. If you find that you are not getting enough of certain minerals then there are supplements available that can help you achieve your goals.
Advertisement
Recommended Reading:
How Often Should Dogs Take A Shower? →
Stay Updated
Actionable growth insights, once a week. No fluff, no spam—unsubscribe anytime.
Advertisement
You May Like
Teeth Pain - Hot Or Cold?
09/03/2025

Will My Abdominal Muscles Disappear If I Stop Exercising?
10/25/2025

Is Onion An Antibiotic?
11/03/2025

The Advantages Of Conscious Consumption And Lifestyle
10/22/2025

Is Carrot Juice Beneficial For The Lungs?
09/17/2025
What Will Affect Your Immune System?
09/26/2025

Is Cucumber Beneficial To The Skin?
09/19/2025

Is Almond Milk Beneficial For The Elderly?
09/17/2025

What Are The Benefits Of Bananas For Prostate Enlargement?
10/07/2025

When Should I Worry If A Dog Vomits?
10/24/2025
The Best Supplement For Healthy Joints
09/13/2025

Five Simple Steps To Relieve Stress And Anxiety
09/18/2025

Can Avocados Dilute Blood?
08/07/2025

How To Use Jewelry To Customize Your Appearance
10/02/2025

How Do I Obtain 1200 Milligrams Of Calcium Per Day Through Food?
10/02/2025

How Often Should Dogs Take A Shower?
09/26/2025

Lunch Has 5 Nutritious Ideas That Can Satisfy You All Day Long
09/17/2025

What Is The First Thing You Must Teach Your Dog?
10/19/2025

What Would Happen If I Drank Aloe Vera Juice Every Day?
09/26/2025

How To Use Braids To Comb Hair
08/06/2025

Five Nutritious Snacks That Satisfy You All Day Long
09/29/2025

Four Simple Methods Of Naturally Improving Mood
09/14/2025

Is Avocado A Cholesterol Rich Food?
10/10/2025

Is It Best To Breathe Through Your Nose Or Mouth While Running?
08/17/2025
Comments
VelvetTelemetry · 10/29/2025
Keeps blast radius contained.
RadiantCipher · 08/05/2025
Liberates focus for higher-order work.
AuroraGlyph · 08/17/2025
This invites action—start now?
VectorPilgrim · 10/01/2025
Who’s benchmarking this?
CircuitNomad · 10/28/2025
Supports mindful debt repayment.